What is Ageing? How and when does it affect our skin? Are there any Products that can help slow down ageing? Read on to find out!
Advertisements, magazine articles, roadside hoardings, etc., have shoved this word down the Indian public’s throat for a long time. But…

Ageing is how the body gradually loses its ability to carry out everyday activities, a slow and steady decline in how well a person functions. Even though we all age, the rate at which we age varies. For example, a 50-year-old man might have a slower pace of ageing than a 55-year-old man. Ageing depends on various factors, including family history, environmental factors, genetic influences, and lifestyle choices.
Ageing is a genetic and natural process that happens to everyone. The positive side of ageing is that it is the process of becoming more mature and confident in how we go about daily life. The negative part of ageing is that it invites skin conditions and decreases energy levels in the body.
Skin is proof that life is all about change. Lifestyle, diet, heredity, and personal habits affect how your skin ages. For example, if you are or have ever been a smoker, the once-healthy oxygen molecules, aka free radicals, have become hyperactive and unstable due to smoking.
Other factors such as light exposure (photoaging) and a lack of subcutaneous support are the leading causes of wrinkled, spotty skin (fatty tissue between your skin and muscle). Stress, gravity, daily facial movement, obesity, and even sleep posture are all factors that contribute to skin ageing.
Let’s understand a few of them in detail:

The skin can be a powerful manipulator when it comes to your skin. Not only does it leave it with sunburn or tan, but excess exposure can be one of the main reasons for premature ageing. Over time, the sun’s UV rays damage certain fibres in the skin called elastin, responsible for your skin’s tautness. The breakdown of these fibres causes the skin to sag and stretch, leaving it unable to snap back into place. Sun damage also causes skin cells to be damaged, which takes longer to heal and causes premature skin ageing.
We have always heard how bad habits can damage our skin, and it is true in the case of smoking. Because not only is the skin of smokers more prone to have wrinkles, but it also reduces the tendency of collagen to be rebuilt. Smoking also interferes with normal blood flow. Thus, the circulation required by the skin to ensure it looks healthy and youthful is absent.


Have you ever woken up with bed sheet marks on your face? Well, weirdly enough, sleeping can also cause ageing. Sleep creases are usually visible on the side of the forehead and cheek due to awkward head positions on the pillow. But fear not! Changing your sleeping position can help alter your rate of ageing.
Have you heard about Laugh Lines? Yes, it’s true. Laughing a lot or over a more extended period can cause these lines on your face to become more prominent, especially around 30 or 40. Lines may appear wherever there are maximum facial movements, like the corners of your mouth, crinkling on your forehead, or vertically on the skin above the top of your nose. So evidently, happiness does come with a price.

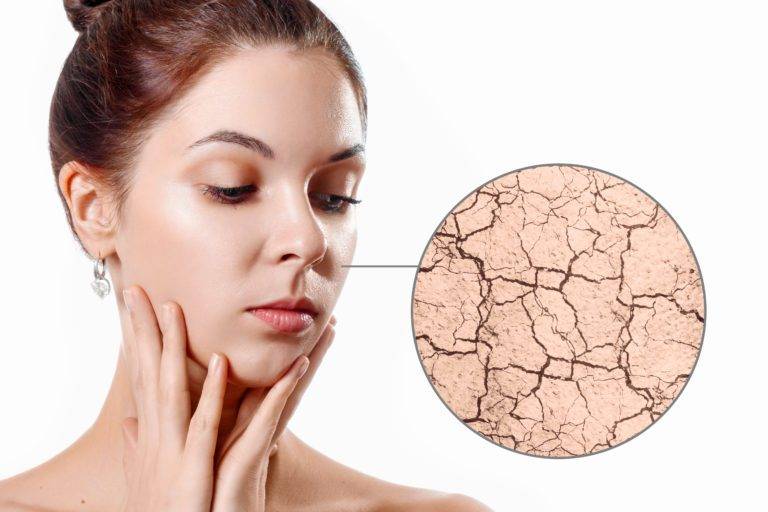
Dryness makes your skin look wrinklier. Individuals above 40 who have dry skin have also lost their sweat or oil glands. As a result, signs of ageing like fine lines and wrinkles become more common. Harsh chemicals and soaps containing astringents further aggravate the issue by dehydrating the skin. Dry skin can also become irritated skin and cause faster ageing.
Although ageing is an unavoidable aspect of life, most of us wish to retain our youth for as long as possible. You can’t stop time, but you can delay the ageing process and lower your risk of age-related disease by making dietary and lifestyle adjustments. The two fundamental causes of ageing are
1. the accumulation of cellular damage caused by free radicals – reactive chemicals, and
2. the shortening of telomeres – structures at the ends of chromosomes that play a crucial role in cellular division.
The most effective approaches to encourage healthy ageing and decrease the effects of ageing on your body are eating a nutrient-dense diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Furthermore, scientists have discovered several chemicals that may help prevent age-related disease by slowing down some ageing processes.
Here are some of the products that may help slow down the ageing process:

Curcumin, the main ingredient in turmeric, has been demonstrated to have significant antioxidant activities attributable to its powerful cellular protective properties. When cells stop dividing, a process known as cellular senescence occurs. Senescent cells develop as you get older, hastening ageing and disease progression.
According to research, curcumin activates proteins that help postpone cellular senescence and improve longevity. Furthermore, studies show that curcumin reduces cellular damage and extends life span, explaining why turmeric is linked to a lower incidence of age-related cognitive impairment. You can get more curcumin by cooking with fresh or dried turmeric or taking turmeric or curcumin supplements.

Crocin is a yellow carotenoid pigment in saffron, a popular and expensive spice used in Indian and Spanish cooking. Crocin has been found in human and animal research to have anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, antidepressant, and anti-diabetic properties. It may also help to prevent cognitive deterioration as people get older.
According to test-tube and mouse studies, crocin helps prevent age-related nerve damage by decreasing the generation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and reactive oxygen species (ROS). Both AGEs and ROS are molecules that contribute to the ageing process. Crocin aids in preventing ageing in human skin cells by lowering inflammation and guarding against UV-induced cellular damage. Because saffron is the most costly spice on the planet, it may be more cost-effective to take a supplement.

Vitamin C protects cells from oxidative damage by acting as a potent antioxidant in the body. It’s also involved in immunological function, inflammatory management, and other vital activities for good ageing. Therefore, it is essential to maintain an appropriate intake of this vitamin to support your health and defend against age-related illnesses. For example, those with greater blood levels of vitamin C did better on tasks involving attention, focus, memory, decision-making, recall, and recognition in a study of 80 adults with an average age of 60.
Vitamin C is also necessary for healthy skin. Supplementing may help hydrate the skin, boost collagen formation, and protect against wrinkles and premature ageing caused by sun exposure. Furthermore, some research suggests that vitamin C supplementation promotes immunological function in the elderly. Since older persons are more likely than middle-aged or younger adults to have suboptimal or insufficient vitamin C levels, they should consider taking supplements. This is especially important when their diet lacks vitamin C-rich foods like fruits and vegetables.
We recommend consulting with a certified medical practitioner before taking any supplements. If you have any questions or want to book a session with our in-house dermatologist, click here to know more!